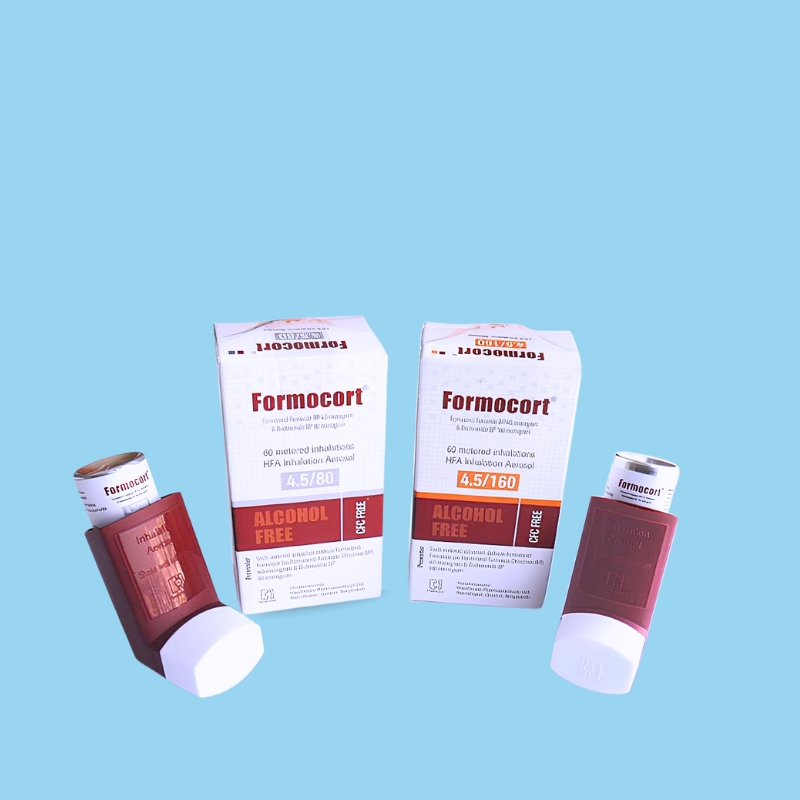
Treatment of Asthma: Formocort® inhaler is indicated for the treatment of asthma in patients 12 years of age and older. Formocort® is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm. Maintenance treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Formocort® 4.5/160 is indicated for the twice daily maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) including chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Formocort® 4.5/160 is the only approved dosage for the treatment of airflow obstruction in COPD.
Formocort® should be administered twice daily every day by the orally inhaled route only. After inhalation, the patient should rinse the mouth with water without swallowing.
Asthma: For patients 12 years of age and older: The dosage is 2 inhalations twice daily (morning and evening, approximately 12 hours apart). The recommended starting dosages for Formocort® are based upon patients' asthma severity. The maximum recommended dosage is Formocort® 4.5/160 mcg twice daily. Improvement in asthma control following inhalation of Formocort® can occur within 15 minutes, although maximum benefit may not be achieved for 2 weeks or longer after beginning treatment. Individual patients will experience a variable time to onset and degree of symptom relief.
For patients who do not respond adequately to the starting dose after 1-2 weeks of therapy with Formocort® 4.5/80, replacement with Formocort® 4.5/160 may provide additional asthma control.
If a previously effective dosage regimen of Formocort® fails to provide adequate control of asthma, the therapeutic regimen should be re-evaluated and additional therapeutic options, (e.g., replacing the lower strength of Formocort® with the higher strength, adding additional inhaled corticosteroid, or initiating oral corticosteroids) should be considered. COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease): For patients with COPD the recommended dose is Formocort® 4.5/160 Inhaler: 2 inhalations; twice daily. If shortness of breath occurs in period between doses, an inhaled short-acting b2- agonist should be taken for immediate relief.
The use of Formocort® is contraindicated in the following conditions l Primary treatment of status asthmaticus or other acute episodes of asthma or COPD where intensive measures are required. l Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in Formocort®.
Caution should be taken in patients with diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, untreated hypokalaemia, severe hypertension and severe cardiovascular disorders, such as ischaemic heart disease, tachycardia or severe heart failure, glaucoma and cataract, hypercorticism. Paradoxical bronchospasm may occur, with an immediate increase in wheezing and shortness of breath after dosing. If the patient experiences paradoxical bronchospasm the medication should be discontinued immediately.
As the combination inhaler contains Formoterol Fumarate and Budesonide, the type and severity of adverse reactions associated with each of the compounds may be expected. There is no incidence of additional adverse events following concurrent administration of the two compounds. Adverse events, which have been associated with Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate and Budesonide, are given below:
Formoterol Fumarate: Tremor, palpitations and headache are common adverse events. Cardiac arrhythmias, muscle cramps and hypersensitivity reactions, including rash, oedema and angiooedema are uncommon and rare. Budesonide: Hoarseness, candida infection in the oropharynx and throat irritation may occur in some patients. Cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions, respiratory tract infections, immunosuppression, growth effect in children, glaucoma & cataract have been reported.
Pregnancy category C. There is no clinical data for the use of formoterol and budesonide on exposed pregnancies are available. Budesonide is excreted in breast milk. However, at therapeutic doses no effects on the suckling child are anticipated. It is not known whether formoterol passes into human breast milk. Administration of drugs during pregnancy and lactation should only be considered if the expected benefit to the mother is greater than any possible risk to the foetus or child.
Co-administration with strong cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir) should be avoided as they may cause increased systemic corticosteroid effects. Co-administration with Monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants should be with extreme caution as they may potentiate effect of formoterol on vascular system. Beta-blockers should be use with Caution as they may block bronchodilatory effects of beta-agonists and produce severe bronchospasm. Co-administration of Formocort with diuretics should be with caution, as they may cause electrocardiographic changes and/or hypokalemia associated with nonpotassiumsparing diuretics may worsen with concomitant beta agonists.
The signs and symptoms of Formoterol overdose are tremor, headache, palpitations, tachycardia, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, prolonged QTc-interval, arrhythmia, nausea and vomiting. Acute overdosage of Budesonide, even in excessive doses, is not expected to be a clinical problem. Chronic overdose of inhaled Budesonide may lead to adrenal suppression.
Pressurised canister, do not puncture, break of incinerate even with apparently empty. Avoid storage in direct sunlight or heat. Store below 30 C. Keep away from eyes. Keep away from childrens.


.jpg)