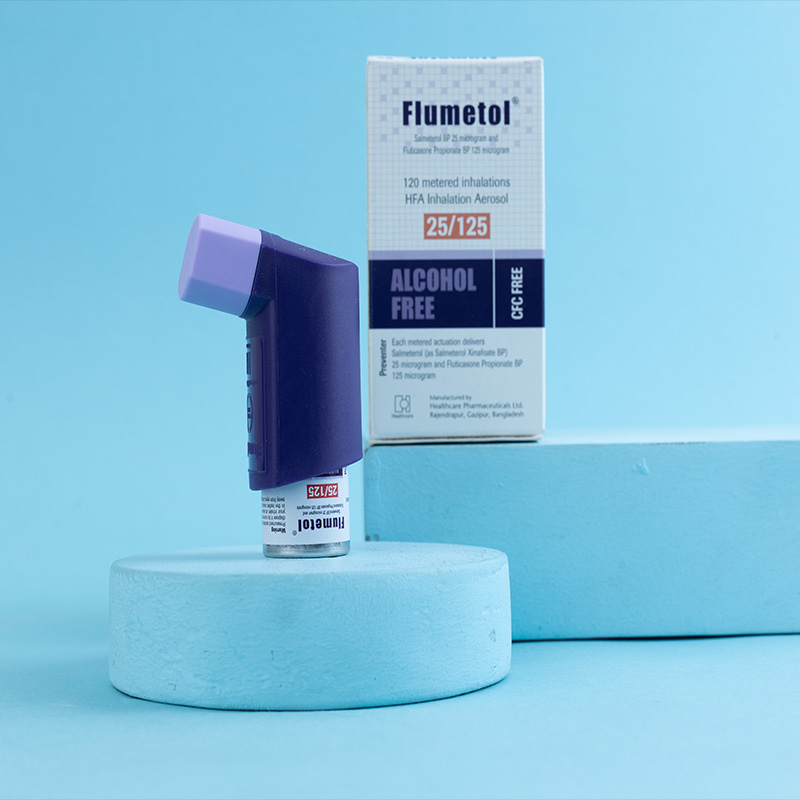
Flumetol® is indicated in the regular treatment of asthma where use of a combination product (long-acting beta-2 -agonist and inhaled corticosteroid) is appropriate: Patients not adequately controlled with inhaled corticosteroids and as needed inhaled short acting beta-2-agonist. or Patients already adequately controlled on both inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta-2-agonist.

Flumetol contains two pharmacologically active agents with complementary actions. Salmeterol Xinafoate is a selective, long-acting beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonist that offers sustained bronchodilation for up to 12 hours by binding to the beta-2 receptors in bronchial smooth muscle. This helps reduce airway resistance and prevent bronchospasm. Fluticasone Propionate is a potent inhaled corticosteroid with high glucocorticoid activity that acts directly on the lung tissue to reduce inflammation, inhibit cytokine production, and improve lung function. When combined, Salmeterol provides symptom prevention while Fluticasone targets the underlying inflammatory pathology of asthma, making Flumetol an optimal solution for long-term disease management with a reduced risk of systemic side effects.

Flumetol is administered via inhalation, either through a pressurized metered-dose inhaler or dry powder capsule device. Adults and adolescents aged 12 years and older typically receive two inhalations twice daily, with varying strengths based on asthma severity. Children between 4 to 11 years are generally prescribed the lowest available dose. The medication should be used consistently every morning and evening, approximately 12 hours apart, to maintain therapeutic levels. The dosage should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical response and severity of asthma.

Correct inhaler technique is crucial for optimal drug delivery. Patients should shake the inhaler before each use, fully exhale, and then seal their lips around the mouthpiece. As they begin to inhale slowly and deeply, they should press down on the canister to release the medication and hold their breath for at least 10 seconds. If a second dose is required, a 1-minute gap is recommended before repeating the steps. After use, rinsing the mouth with water helps reduce the risk of oral candidiasis. Regular cleaning of the inhaler mouthpiece is advised by removing the canister, rinsing the actuator under warm water, drying it thoroughly, and reassembling it properly.

Flumetol is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to Salmeterol, Fluticasone, or any of the formulation components. It is also not intended as a primary therapy for acute asthma attacks or status asthmaticus where intensive treatment is needed.

Flumetol should not be initiated in patients experiencing worsening or unstable asthma. It is not suitable for the immediate relief of acute bronchospasm; patients should always carry a fast-acting short-acting beta-2 agonist inhaler for emergency use. Paradoxical bronchospasm may occur and, if observed, treatment should be discontinued immediately. Prolonged use of high-dose inhaled corticosteroids may result in systemic effects such as adrenal suppression, reduced bone mineral density, or growth retardation in children. Use in patients with cardiovascular disorders, seizure history, or hyperthyroidism should be approached with caution. Monitoring is also advised in COPD patients due to the increased risk of pneumonia associated with inhaled corticosteroid use.

There is limited clinical data on the use of Salmeterol and Fluticasone during pregnancy and lactation. Flumetol should only be used in these populations if the potential benefits clearly outweigh any possible risks to the fetus or nursing infant. Although systemic absorption is low with inhaled therapy, it is recommended to monitor both mother and child if treatment is initiated during these periods.

Clinically significant interactions are unlikely due to low systemic absorption. However, co-administration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ketoconazole or ritonavir may increase systemic exposure to Fluticasone and should be approached with caution. The use of non-selective beta-blockers is generally contraindicated in asthma patients due to the risk of bronchospasm.

Adverse reactions to Flumetol are consistent with those of its individual components. Salmeterol may cause tremors, palpitations, headache, or muscle cramps, especially when therapy is initiated, but these effects typically diminish over time. Cardiac arrhythmias may occur in predisposed individuals. Fluticasone may lead to hoarseness, oral thrush, and, in rare cases, systemic corticosteroid effects with prolonged high-dose use. Hypersensitivity reactions such as rash or facial swelling have been reported. Mouth rinsing after each dose can reduce the risk of local adverse effects.

In the event of an overdose, Salmeterol may produce symptoms such as tachycardia, tremor, hypokalemia, or hyperglycemia. Fluticasone overdose is less likely to cause acute toxicity but may lead to transient adrenal suppression. Supportive care is recommended in both cases, including symptomatic treatment and temporary cessation of the drug if needed. Inhaled therapy should be resumed only under medical supervision.

Flumetol should be stored in a cool, dry place below 30°C, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The pressurized canister must not be punctured, burned, or exposed to high temperatures even if empty. Keep the inhaler out of reach of children to ensure safety.