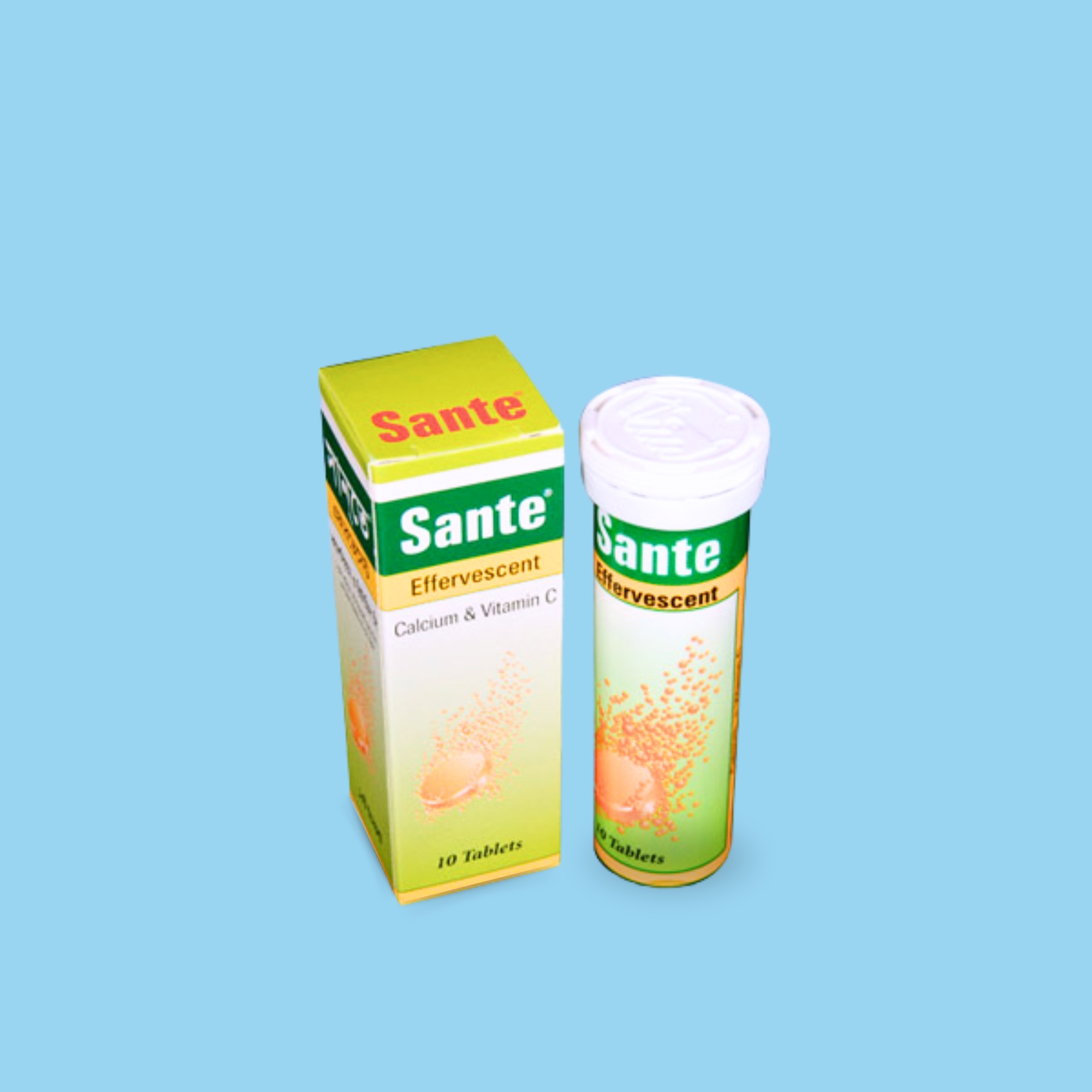
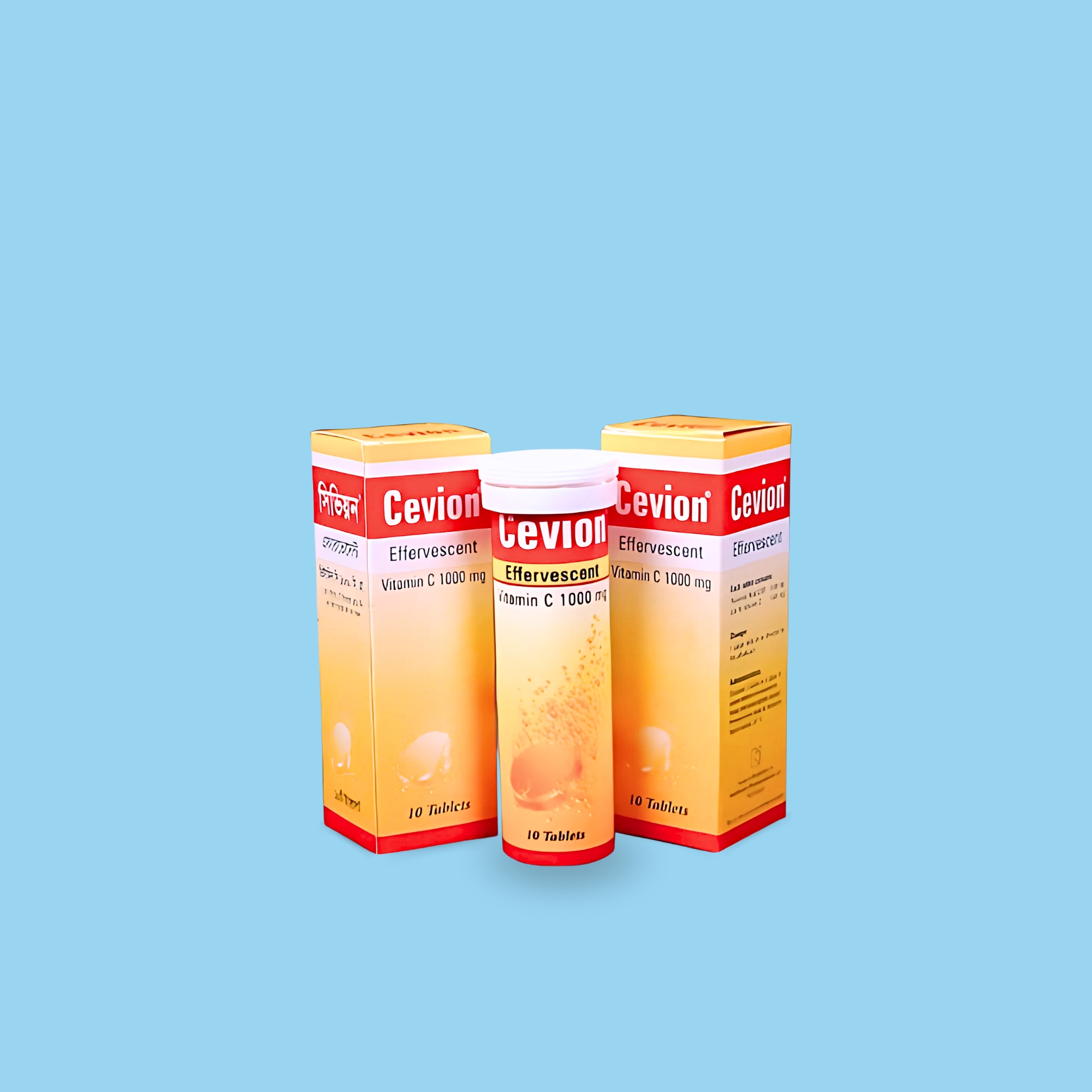
Calcium is used as a pharmacologic agent in humans almost entirely to remedy deficiency. Adequate calcium in the blood is vital to a wide variety of bodily functions, and our internal biochemistry will not tolerate a deficiency, even for short periods. Vitamin C is an essential component of the diet, as humans cannot synthesize vitamin C. It is a very powerful reducing agent and plays an important role in the body’s response to stress. It is also important in the defense against infection.

Calcium is used as a pharmacologic agent in humans almost entirely to remedy deficiency. Adequate calcium in the blood is vital to a wide variety of bodily functions, and our internal biochemistry will not tolerate a deficiency, even for short periods. Vitamin C is an essential component of the diet, as humans cannot synthesize vitamin C. It is a very powerful reducing agent and plays an important role in the body’s response to stress. It is also important in the defense against infection.

Calcium & Vitamin C are indicated in:
Increased demand for calcium and Vitamin C, e.g., pregnancy, lactation, periods of rapid growth (childhood, adolescence), and old age
During infectious diseases and convalescence
Treatment of calcium and Vitamin C deficiency
Osteoporosis
Premenstrual syndrome
Postmenopausal problems
As an adjuvant in colds and influenza

Adults and children of school age: 1 effervescent tablet daily
Children 3 to 7 years: 1/2 effervescent tablet daily
Infants: As prescribed by the physician

In rare cases, mild gastrointestinal disturbances (bloating, diarrhea) may occur. In predisposed patients, prolonged treatment with high doses may promote the formation of calculi in the urinary tract.

For patients with mild hypercalciuria (exceeding 300 mg = 7.5 mmol/24 hours), mild or moderate impairment of renal function, or a history of urinary concrements, monitoring of calcium excretion in the urine is required. If necessary, the dosage should be reduced or therapy discontinued. High doses of vitamin D and derivatives should be avoided during treatment with this preparation unless specially indicated.
Since citrate salts have been reported to increase aluminum absorption, Sante®, which contains citric acid as a constituent, should be used with caution in patients with severely impaired renal function, especially those receiving aluminum-containing preparations. Diabetic patients should take the sugar content into account.

Epidemiological studies with oral calcium have shown no increase in the teratogenic hazard to the fetus. Although supplemental calcium may be excreted in breast milk, the concentration is unlikely to be sufficient to produce any adverse effect on the neonate. Vitamin C may be taken safely during pregnancy and lactation.

Hypercalcemia (e.g., in hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D overdosage, decalcifying tumors such as plasmacytoma, bone metastases); severe hypercalciuria; severe renal failure.
Patients with hyperoxaluria, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, or iron overload. Larger doses may lead to gastrointestinal tract upset.

Potentially hazardous interactions:
Digoxin, tetracycline, furosemide, pentagastrin
Aminophylline, bleomycin, erythromycin, lactobionate, nafcillin, nitrofurantion, conjugated estrogens, sulfasalazine, diethanolamine, chloramphenicol
Potentially useful interactions:
Vitamin D, oxytocin, and prostaglandins
Vitamin C enhances iron absorption

Acute overdosage has not been reported. It would be expected to cause gastrointestinal disturbances but not result in hypercalcemia, except in patients treated with a very high dosage of vitamin D and derivatives.

Keep the tube tightly closed
Protect from heat and moisture
Store below 30ºC
Medicine: Keep out of reach of children